Critical thinking is the ability to analyze and justify problems. It relies on evaluating sources of information such as data, facts, observable phenomena, and research results.
We live in a world saturated with information of varying quality and relevance. To be an effective critical thinker, one need to focus on own purpose and context, avoid information overload, and keep your own thinking in perspective.
Critical thinking is determined by the following factors:
Challenging the source: Challenging sharpens your thinking, selects the most pertinent information, and prepares it for further analysis and evaluation.
Argument identification: Arguments are everywhere. Whenever someone tries to show that something is true or to persuade someone else to agree with you, you can identify the argument. As a presenter, identify the argument You'll find abilities to be one of the most useful critical thinking skills.
Analyzing Sources and Arguments: To analyze something means to examine it, explain it, and interpret it. Critical thinking requires being able to examine sources, arguments, theories, and processes and explain how they work. Good analysis also involves examining, interpreting, and explaining the interplay of evidence, arguments, assumptions, methods, claims, and arguments.
Evaluating the Arguments of Others: Evaluating should consider and explain the relative strengths and weaknesses of the sources and the arguments they present. You must be able to evaluate the arguments, the claims that support those arguments, the evidence that supports those claims, and the reasoning that ties them all together.
Create Your Own Argument: To create an argument, you need to piece together the evidence, arguments, and claims to create your own main thesis. Composing arguments is also called composition, which means "putting things together". As you create your arguments, summarize the insights you gain from your analysis and evaluation. We will also explore how to apply your own critical thinking to a broader context and the new insights and perspectives it brings.
You may be wondering how programming can help you with critical thinking. Critical thinking may seem fairly common, but its importance is often underestimated. However, programming is widely recognized as one of the best tools for teaching critical thinking, thanks to its authentic, down-to-earth approach. Here are some reasons why coding helps with critical thinking:
1. Similar Approaches to Problem Solving: Coding and critical thinking share the following process steps:
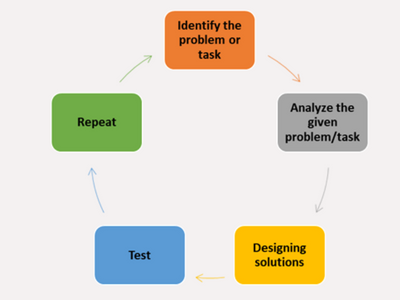
A good example of this coding process is troubleshooting. This is because programmers must identify problems and try different tactics until they find a strong solution.
2. Practice first: Coding encourages rethinking by approaching a problem from different perspectives and finding as many possible solutions as possible. This repetition during the coding process allows students to practice critical thinking skills in each lesson.
3. Keep an open mind: What if there is no right answer to a problem? In coding, this is a fairly common scenario because there are multiple correct answers in the coding process. For example, each website, animation, or game will differ based on your design aesthetics, functionality, and available technology. This variability exposes students to the reality that they must remain open to new ideas and remain flexible.
Research says that
-
Students with computer programming experiences are said to typically score higher on various cognitive ability tests than students who do not have programming experiences.
-
Coding literally has one use syntax and semantics to deal with problems and a coder’s job also requires perseverance, which means that he / she has to keep going when even they come across an obstacle.
-
When you come across a dead end in coding, there’s always a way you can go back and start again.
There are two ways to teaching coding:
Unplugged Activities:
-
Unplugged activity aims to teach programming concepts through the use of games or activities that can be done offline using tangible objects, such as paper and markers.
-
Offline coding is a good way to engage younger students without the use of technology.
-
It helps students better understand computer science
-
concepts through role-playing, analogies and other visual exercises.
Examples of unplugged activities are
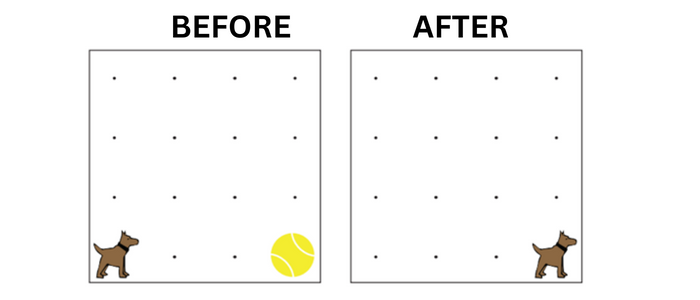
Here in this activity the Dog Tracy should change its position from first image to second image. Children should write steps to achieve this. The only problem here is that the Dog can move Forward, Move Left, Take Ball and Put Ball.
So, the code to achieve the required output is:
Step 1: Move Forward
Step 2: Move Forward
Step 3: Move Forward
Step 4: Take Ball
In the second activity children need to write code in the form of symbols to create the grid as shown in the first image
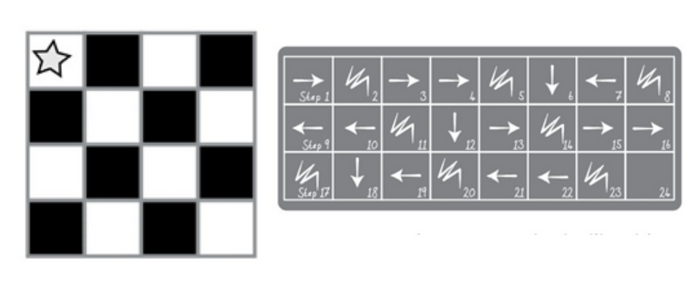
Second image shows the code written in the form of symbols
Plugged Activities:
For plugged activities you can write code on computer using any programming languages like C, C++, Java, Python or any other language available in the market.
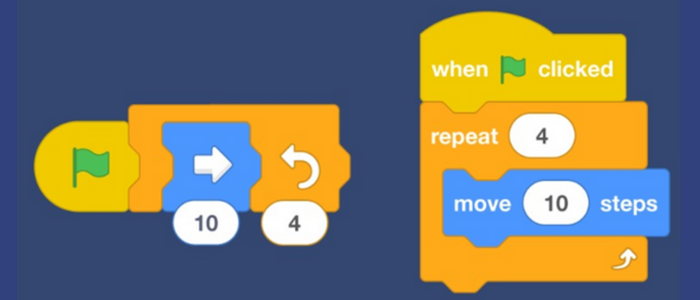
Block coding is very easy and children from lower grades can start learning coding on Block coding platforms like Scratch, Makecode etc. For children from higher grades they can choose any programming language like C/C++ , Java , Python etc.

Coding is constructive in nature and it helps to develop persistence, communication, creativity, and higher-order thinking.
Yes, coding also helps children to become future ready and become capable to solve all those problems that we have not yet dreamt of today.
Cyber Safety Initiatives by NexSchools
School Children Making A Difference With Blogs